Crafting Your Product Management Path: 7 Unconventional ideas
Last updated on Fri Sep 13 2024
The success and well-being of a product largely depend on effective product management. In product management, we create, develop, and improve a product to ensure both customer satisfaction and brand growth. However, like other business concepts, traditional methods should evolve, giving way to alternative ideas that may break conventional norms. Growing businesses should be willing to take risks, which also applies to product management.
We have compiled 7 unconventional, alternative ideas for product management that you can implement in your business. For proper context, we’ll explore how product management has evolved, the limitations of traditional methods, and more.
How Did Product Management Evolve?
The origin of product management dates back to the 1930s, making it relatively modern compared to other business concepts. Since then, product management has undergone changes, shaping up to become what we know today.
Product managers now collaborate with other experts, such as engineers, because our technological world requires digital expertise for product management. They may also learn basic coding, which wasn’t necessary in the past (and may not be in the future with AI coding).
The world continues to progress, revealing the need for updated strategies for product management. This is particularly true due to technological advancements and the ever-changing culture.
The Need for Unconventional Product Management Tactics
Why do we need new tactics? Are traditional models obsolete? Not necessarily. However, new developments bring a different set of challenges, which calls for changes. For example, the growth of Artificial Intelligence has led to discussions about its integration into mobile apps and other digital products. It also performs some tasks and paves the way for fresh insights.
This does not mean we must abandon every traditional idea. Many time-tested techniques remain relevant today. However, we are neither bound by the old ways nor neglectful of them. We consider their limitations and think outside the box.
For insights on managing feedback effectively, consider our guide to customer feedback management for SaaS.
Limitations of Traditional Methods
Some limitations of traditional methods are:
Rigid Procedures
Due to the step-by-step process involved in many traditional frameworks, there is little room for flexibility. You must complete one process before moving on to the next, and changes may be disruptive. Given that various factors can cause changes, this limitation can lead to frustration.
For example, the Waterfall method does not accommodate spontaneous shifts. Implementing a feature prioritization matrix might offer more flexibility.
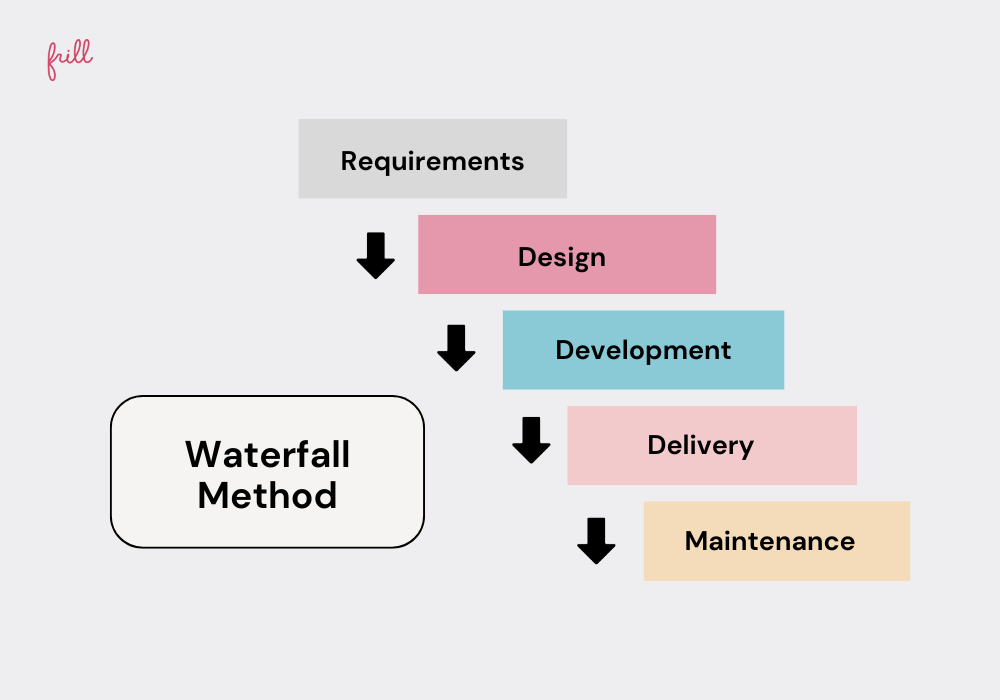
Hinders Decision Making
Due to their structures, traditional methods often take longer to plan, which can slow down decision-making. This becomes problematic when quick decisions need to be made and implemented, especially during market changes. Traditional methods also involve bureaucracy, multiple layers of approval, and difficulties in altering fixed plans.
High Risk
Traditional methods of product management have a complex relationship with risk. On one hand, their structured approaches are designed for caution, which can sometimes stifle creativity. On the other hand, their rigid structure makes it challenging to recover from failure.
7 Unconventional Product Management Ideas
Having evaluated the need for alternative methods and some limitations of current ones, below are 7 fresh ideas to better manage your product:
1. Pretotyping
Not to be confused with prototyping, pretotyping serves a different purpose. While prototypes are test versions of a product, pretotyping is conducted before creating a prototype. The goal of pretotyping is to determine whether the public will react positively to the product.
A pretotype is a simulated version of the product or a basic format. Pretotyping is less costly, allowing you to prevent potential wastage if users suggest different changes. Pretotyping can also enhance your roadmapping strategies.
Pretotyping follows the formulation of an idea. First, you choose a pretotype. Next, set a hypothesis about how users will engage with the product. Finally, test the hypothesis using the pretotype and learn from your findings.
2. Lean UX
The major goal of lean UX is to break down the creation process into manageable steps, rather than aiming for a perfect idea before starting. The design is implemented gradually on the product, allowing for regular feedback at every step, which helps reduce mistakes. It also encourages flexibility, as changes can be made at any point in the process.
Additionally, its gradual approach promotes teamwork, as teams work interdependently, addressing a common complaint of traditional methods.
3. Impact Mapping
Impact mapping is a planning technique that helps teams integrate different actions to achieve a goal. It begins with defining your desired results—what do you want to achieve? Once the goal is defined, specify who the actors will be.
In this context, actors are those who either work toward achieving the goal or are affected by it. These actors will impact the goal in various ways. Impact mapping also involves detailing the actions you will take to ensure the goal is met.
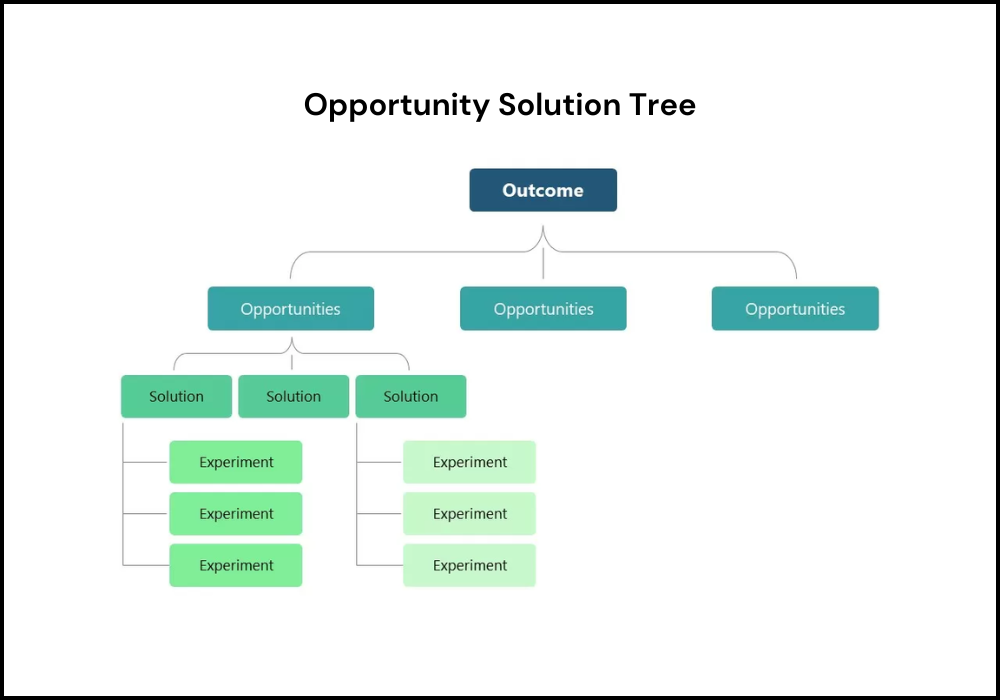
4. Opportunity Solution Tree
The name reflects its purpose. The Opportunity Solution Tree aims to analyze opportunities and seek solutions. It is designed to solve problems with a visual approach, making this technique appealing to many.
Like a physical tree, the Opportunity Solution Tree starts with the root, which contains the desired outcome. Then comes the opportunity space, which addresses customers' needs and pains. The solution and assumption spaces cover potential solutions and evaluate these solutions.
5. Innovation Games
Innovation games are also designed for teams, similar to some of the previously mentioned ideas. An innovation game uses creativity and fun to encourage team members to solve problems, generate new ideas, and make decisions.
Innovation games elevate unconventional methods, making them ideal for spontaneous, creative individuals. They remove pressure from teammates and stimulate creative thinking. Methods used include role-playing, brainstorming, and scenario planning.
Read more on how to effectively collect and engage with feature requests.
6. Platform Thinking
To understand platform thinking, compare it to traditional methods. In a traditional business model, you sell a single product or service.
Platform thinking breaks this mold by suggesting the creation of a platform that connects product developers to the target market. This setup allows for interaction and value sharing, facilitating direct feedback.
Some brands already use this technique to great success. An example is Glassdoor. Discover more about implementing SaaS feedback strategies.
7. The 10x Rule
The 10x Rule was popularized by Grant Cardone, an entrepreneur. Its premise is simple: Set goals ten times higher than you originally imagined and take actions that are also ten times greater than your initial plan. The aim is to set your targets so high that even if you miss them, you’ll still achieve significant results.
Google implemented this strategy when developing their search engine, aiming to surpass Yahoo and others.
Conclusion
Do these ideas seem new, unusual, or even a bit daunting? If so, you’re in a good place! Sometimes, it takes unconventional methods to breathe new life into a stagnant workspace. Tailor these techniques to fit your company’s needs, and feel free to develop your own innovative approaches. For more game-changing ideas, check out our post on idea tracking for SaaS and digital businesses.