Understanding User Feedback: How To Collect and Analyse It Effectively
Last updated on Mon Sep 09 2024
User feedback makes the difference between corporations that satisfy their customer’s needs and those that accumulate negative reviews or even lose users. If the customer is to be served and prioritized above making a profit, their feedback is like gold.
User feedback is also important if an organization wants to remain the most sought-after for a particular product. Products of high quality are tied to an organization's ability to gather and handle feedback.
This article is designed to provide you with the necessary knowledge on understanding user feedback, as well as other aspects such as gathering it, making proper analysis to gain the good and discard the bad, and then ways to use this feedback to improve your feedback.
Read on to find out more.
What Is User Feedback?
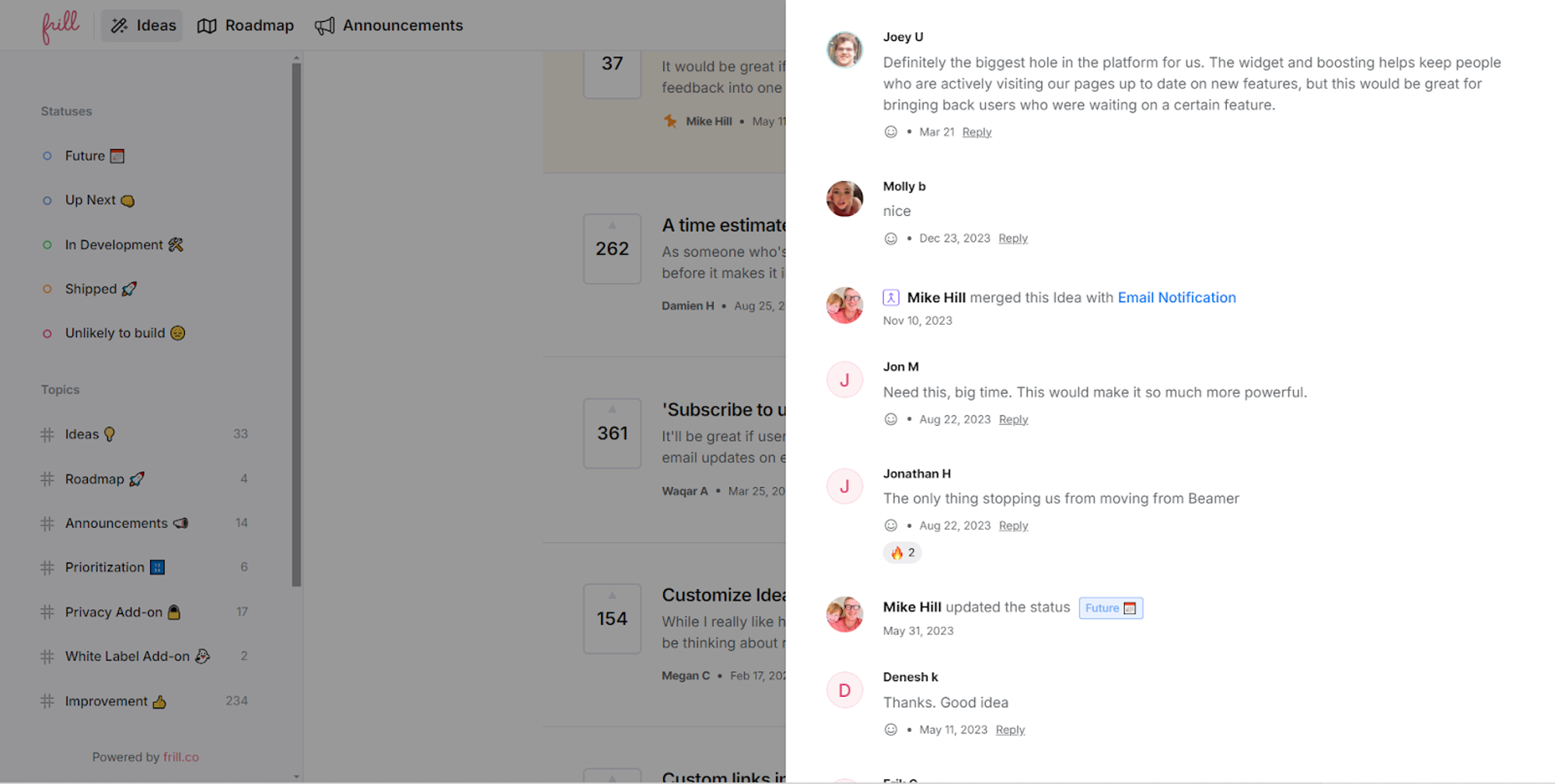
User feedback can simply be defined as hearing from the audience. It involves collecting user opinions, ideas, problems, criticisms and suggestions about a product or service. User feedback aims to ameliorate or improve the product and service.
Feedback comes in many ways, such as recommendations for new features, reporting problems or bugs to be fixed, the product’s usability, and level of satisfaction.
Again, a business that wants to grow and be known for high-quality products must prioritize user feedback. It is non-negotiable. Businesses that offer services also need user feedback.
Why Is User Feedback So Important?
For starters, user feedback sheds light on key areas where an upgrade is needed, encouraging innovation.
It also gives the manufacturers an idea of how customers view the product, lest they remain blinded to the needs of the public. When properly gathered and implemented, user feedback forges the bond between an organization and its customers, like a couple that regularly communicates.
Organizations that provide avenues for users to express themselves will gain loyalty and trust. Picture the competitive advantage for the organization!
A product’s relevance and longevity in the market depend largely on user feedback, especially in a fast-paced industry. The market never remains stagnant, with new products appearing by the second. Ergo, any business that desires to make a profit for a long period must get to the heart of customers. The most significant way to achieve this is by gathering feedback.
Finally, no product remains at its highest level for long. Issues develop, and getting user feedback prevents these issues from escalating and harming the company’s progress.
What Are the Different Types of User Feedback?
For maximum results, gather various feedbacks, as opposed to one kind. This enables better analysis of the data you get from customers.
Feature request is one of the most common types of user feedback, but there are a lot more. Below is a list of the different types:
1. Feature Requests
Feature Requests, as the name implies, cover suggestions from users on new features to add to a product. Sometimes, they may simply ask for improvements on features already there.
Feature requests are direct, making them crucial for product development. With this type of user feedback, you gain clarity on the user’s personal needs and desires. Acknowledging feature requests can also make customers feel important, translating to loyalty.
Even better, feature requests reveal the customer’s desire to see your product improve, and who would not want that?
2. Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Source: mTab
Net Promoter Score (NPS) differs from feature requests in its directness, but it is highly effective in determining customer loyalty. To gather this type of user feedback, simply ask, "How likely are you to recommend this product/service to others?"
The Net Promoter Score uses scales, ranging from 0 to 10. Customers who score 9-10 are promoters, equivalent to marketers. 7-8 are classified as passives, meaning they simply use the products without recommending them. 0-6 are the detractors, who may switch from your products.
Every organization aims to have numerous 9-10 scores and little 0-6. When high, it reflects strong customer satisfaction. Conversely, a low NPS means you have work to do. This feedback type is useful to have a general idea of customer loyalty and the public’s reception of your product. Through NPS, you can note areas needing improvement.
3. Bug Reports
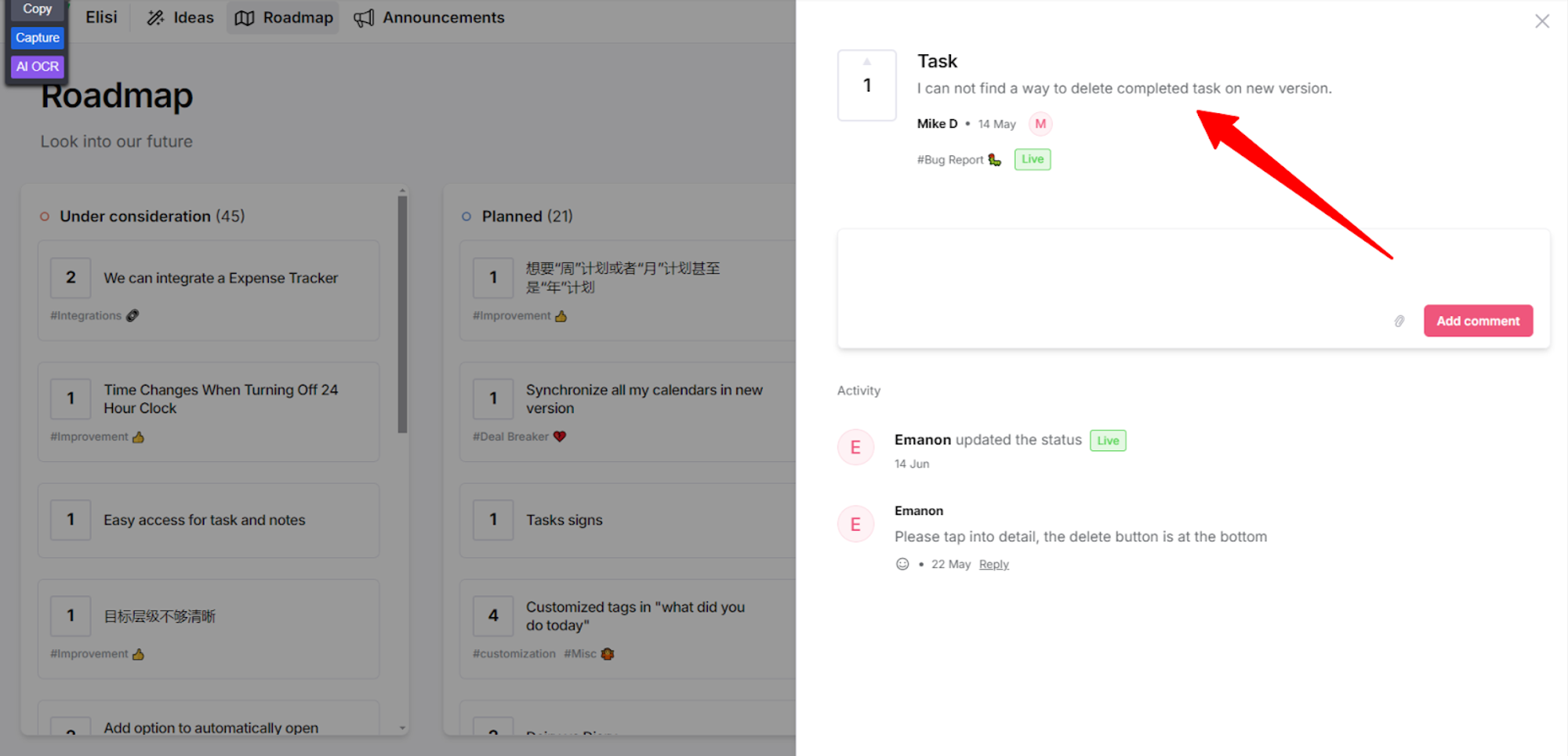
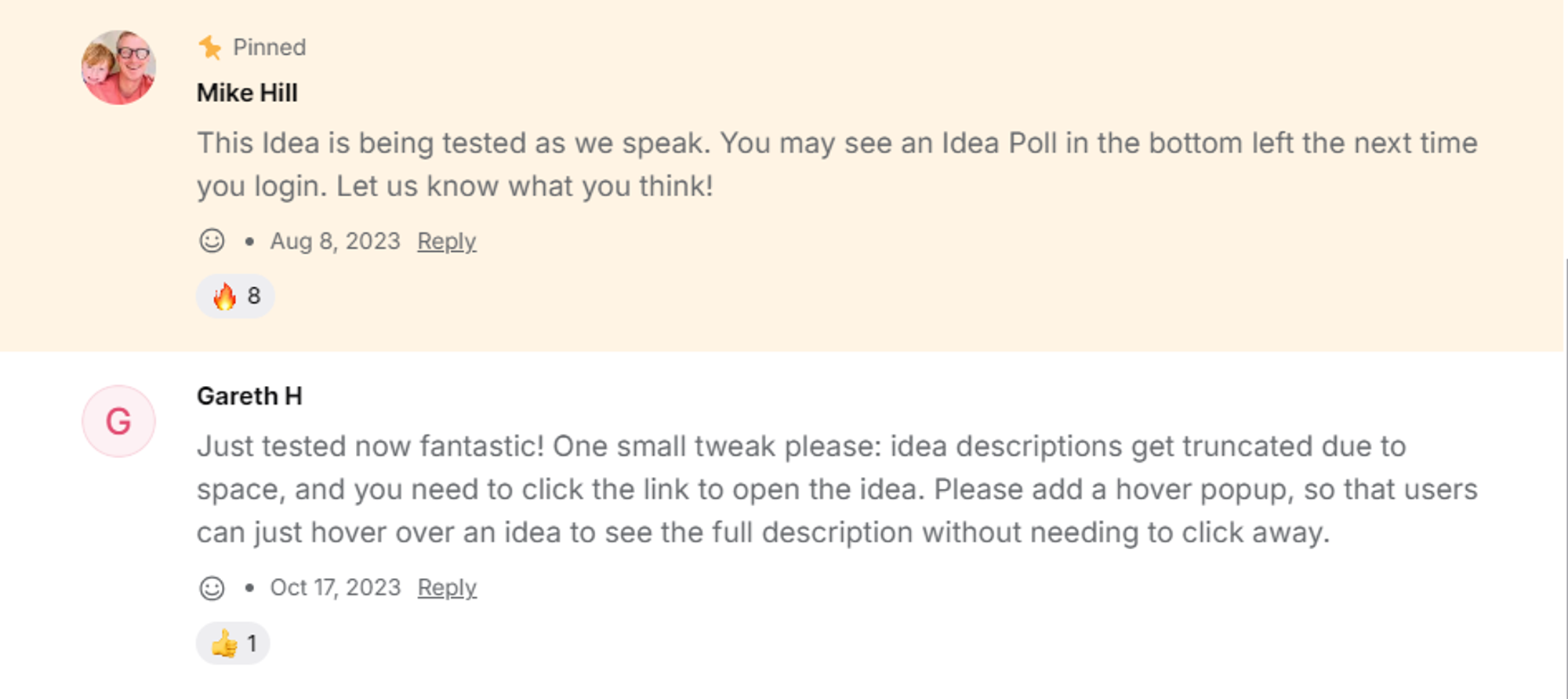
Bug Reports are also common and useful for detecting faults. Even the best products can develop glitches, and thoughtful users would report these problems. After all, they want to enjoy what they purchase.
These reports often go to the development team, who then work to identify and fix the highlighted problems. Some of these faults could have escaped internal testing.
Bug reports can appear under negative reviews and may sound critical, but they are gems and can result in customers’ feeling appreciated. You should treat bug reports as emergencies, as a quick response can foster user trust.
4. New Release Feedback
New Release Feedback is necessary after a new product has been launched, as well as an update or a different version of the product. Launching a product is one task, evaluating its performance is another. New Release Feedback helps with the latter.
New Release Feedback provides answers to questions such as, “Did my product meet customer expectations?” Here, the users state how satisfied they are with the new product. If it’s an update or a new version, they may compare it with older models. The goal is for the new version to supersede the old.
Businesses can use this feedback to make improvements on new products and updates.
5. Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) revolves around the satisfaction of the overall product. Like the New Promoter Score, it uses scales, but the goal is different. CSAT aims to measure how satisfied users are with your product or service. Its scale ranges from 1 to 5 or 1 to 1o, with 5 or 10 being the highest score. A high CSAT is what businesses should target as that implies loyalty, trust and the likelihood of recommendations. On the other hand, a low score is a red signal.
How To Collect User Feedback?
Collecting user feedback is easy, with the right tools. Here are some of these tools and how they typically work:
● In-App Tools
In-app tools are “in-app”, suitable for software and mobile applications. Because they come with the product, users find it easier to provide feedback, which increases the likelihood that they will.
They also give their feedback as they use the product, ensuring a high degree of sincerity. Examples of in-app tools are pop-up surveys, feedback buttons, and interactive widgets. The aim is to encourage users to give opinions, so you must ensure in-app tools users without becoming a nuisance.
● Public Feedback Portals
With public feedback portals, users share their thoughts, suggestions, and experiences on online platforms, available for public viewing. Because of their public nature, users can vote or comment on feedback
These portals enable the organization to know which issues require more priority and which feedback is unhelpful. It also creates a sense of belonging or community that in-app tools may not achieve.
If you prefer qualitative data over impersonal, quantitative results, public feedback portals are crucial.
● Email Surveys
Email surveys may seem outdated and traditional, but do not discard them just yet. Because they allow for direct contact with users, email surveys can offer a personal touch that improves customers’ loyalty.
It is also helpful if you prefer flexible responses. Email surveys can target specific user segments, ensuring more detailed and useful feedback. With email surveys, you can gather both quantitative and qualitative data, expanding your results. They are particularly useful for people who don’t engage in public service portals and are suspicious of in-app too.
● Forms
Feedback forms seem simple, but are highly effective. They can gather feedback from both new and seasoned customers, as well as their experiences with updates.
Forms can be customized to get exact answers or detailed information, depending on your needs. They also make analysis of feedback easy, especially when you collect quantitative data.
It is useful if you prefer formal responses, avoiding the challenges that come with informal interactions.
● Social Media Monitoring
Do you want spontaneous, raw, unfiltered feedback? Social media monitoring is ideal. It involves following users' posts, comments, reviews and even unhindered discussions about a product.
You need a thick skin for social media monitoring as some users are nasty, but the reward is worth it. Social media monitoring also enables the business to keep up with industry trends and get realistic sentiments about a product, which may be hidden in other forms. You can also engage with customers, suitable for growing brand loyalty.
Read more about effective collection methods in our Guide to Customer Feedback Management.
When To Collect User Feedback?
Do not waste time in collecting feedback as timeliness is essential. Feedbacks are also needed in different steps, starting from the period after onboarding. You would need feedback during updates, customer support interactions, random moments, when a user cancels, after user milestones, and during beta testing.
After Onboarding:
Gather feedback after a new product is launched to know how effective the onboarding process is. ****Here, you can identify pain points, struggles and complaints from new users.
Following Updates:
Updates bring changes, and any good business should ensure that the users love these changes. Feedback after an update provides insight into whether the update meets user expectations. It also highlights unforeseen issues.
During Customer Support Interactions:
Customer support interactions can draw in or push away a customer, so you should analyse the quality of support provided and identify any recurring issues.
At Regular Intervals:
Besides milestones, you can schedule moments for feedback. To the user, it may appear random, but you should make plans beforehand. These regular feedbacks allow you to track changes in user satisfaction and address any emerging trends or concerns promptly.
When a User Cancels:
Users cancelling may be difficult, but you can transform those lemons by getting feedback from the outgoing customers. You can use this informations to maintain the customers you still have and even cause a change of heart.
After User Milestones:
User milestones include completing tasks or achieving goals. After they have done these tasks or goals, ask for feedback. You’ll need it to optimize the user experience and ensure that the product continues to meet their evolving needs.
During Beta Testing:
Beta testing is a critical phase for gathering detailed feedback before a full-scale launch. Feedback from beta testers helps identify bugs, usability issues, and feature gaps, allowing you to refine the product before it reaches a wider audience.
Conclusion
Customers are crucial to the success of any business, and their opinions should matter. The best businesses want to both make a profit and serve the common good. The stone that can kill these two birds is customer feedback. Understand the types of feedback, how you should collect them and when you should so you can draft your unique strategy to interact with your customers. To reiterate, feedback leads to product improvement, brand loyalty, high customer satisfaction, and the longevity of a product.
FAQ
Why Is User Feedback Important?
User feedback offers direct insights from users, helps enhance satisfaction, guides development, builds loyalty, and spurs innovation.
What Are the Main Types of User Feedback
The main types include Feature Requests, Net Promoter Scores, Bug Reports, New Release Feedback, and CSAT.
How Can I Collect User Feedback Effectively?
Use in-app tools, feedback portals, email surveys, forms, and social media listening to collect feedback effectively. For more strategies, check out our Customer Feedback Tools.
When Is the Best Time To Collect User Feedback?
Key moments include after onboarding, post-updates, during support interactions, regularly, upon cancellation, at user milestones, and during beta tests.
How Do I Encourage Users To Provide Feedback?
Simplify the process, offer incentives, clearly communicate how feedback will be used, and show how input leads to improvements.
How Can I Ensure That the Feedback I Collect Is Useful?
Ask specific questions relevant to your goals, segment your users, and use qualitative and quantitative methods for a complete feedback picture. For more insights, visit our Product Management Process guide.