Growth Teams and Customer Feedback
Last updated on Mon Aug 19 2024
All teams within customer-centric organizations depend on customer feedback to solve real customer problems.
However, each team interprets this feedback differently:
Product teams focus on specific product parts.
Marketing teams want insight into product benefits and value propositions.
Customer support teams look at satisfaction related to their interactions.
In the last decade, growth teams have surfaced, blending product and marketing roles such as marketers, product managers, designers, and engineers.
The Difference Between Growth and Product Teams
Growth teams and product teams play distinct yet complementary roles in a company. While both are focused on the product, their goals, approaches, and metrics for success are different.
Product Teams are primarily focused on innovation and the development of new features, products, or services. They are responsible for taking ideas from concept to launch, designing and developing new components, and ensuring high product quality. Their success is measured by metrics such as feature adoption, product quality, and customer satisfaction. Product teams typically work on long-term projects with clear milestones, like creating new checkout flows or building entirely new product offerings.
Growth Teams, on the other hand, are focused on optimizing existing features to drive user acquisition, retention, and overall business growth. They run experiments and make data-driven decisions to improve user experiences and streamline processes. Their success metrics include user growth, retention rates, and revenue growth. Growth teams operate with an agile approach, iteratively making improvements based on data and testing. For example, instead of creating a new checkout flow, they might work on streamlining the existing process to reduce friction and improve conversion rates.
How Growth Teams Work
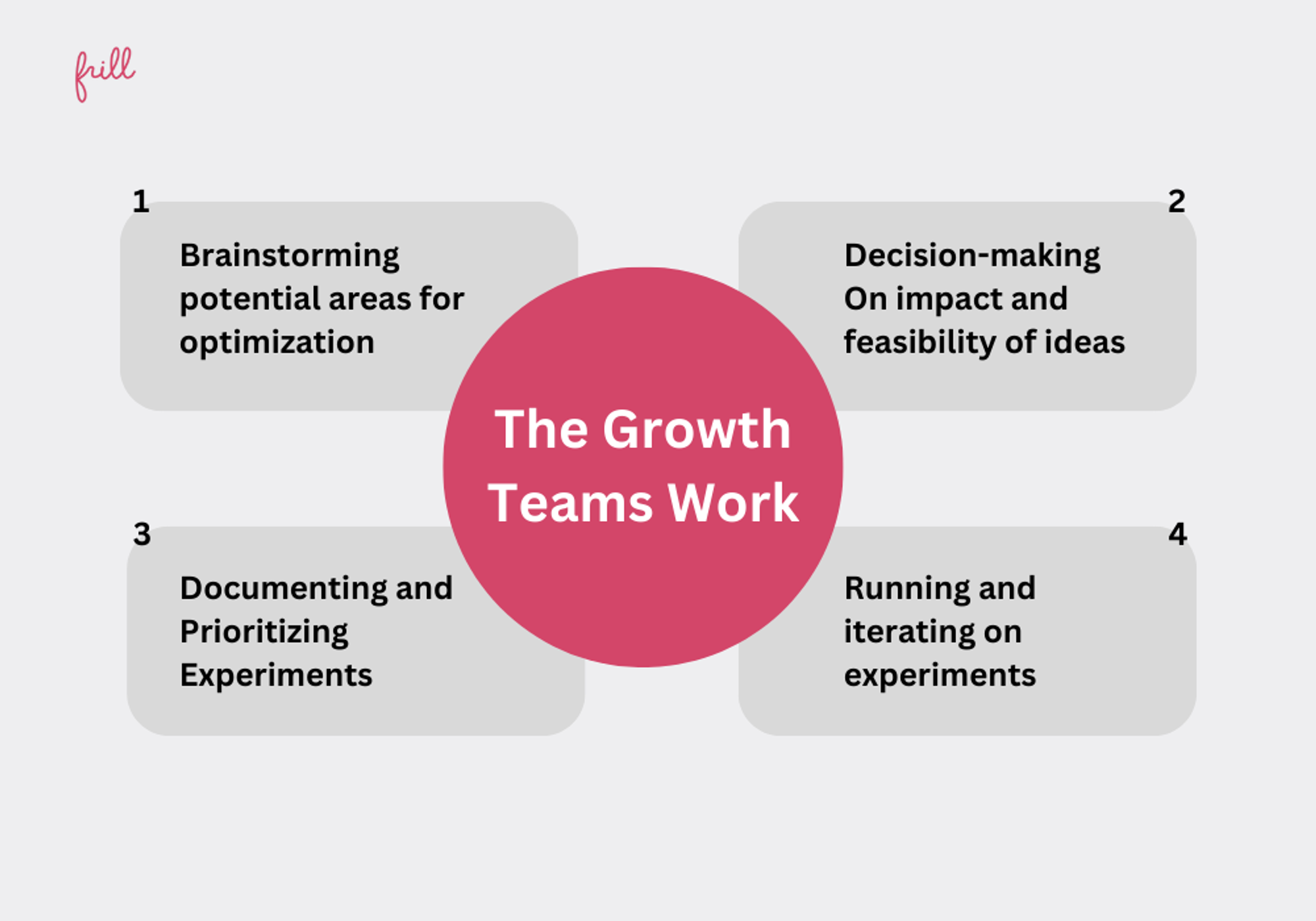
Growth teams operate through a structured, four-step process each quarter, focusing on continuous improvement and experimentation.
Brainstorming Improvement Areas:
At the start of each quarter, the team gathers to brainstorm potential areas for optimization, drawing on data, user feedback, and trends. The aim is to generate a list of high-impact areas to enhance, such as improving user onboarding or reducing churn.
Selecting Focus Areas:
The team then evaluates these ideas, prioritizing the most promising based on potential impact and feasibility. This decision-making is guided by key performance indicators (KPIs) and aligns with the company’s overall goals.
Documenting and Prioritizing Experiments:
Once focus areas are selected, the team documents and prioritizes a set of experiments designed to test hypotheses and drive improvements. Each experiment is carefully planned with clear goals and success metrics.
Running and Iterating Experiments:
Throughout the quarter, the team conducts these experiments, gathering data and insights to inform future strategies. As results come in, they iterate on existing experiments and prioritize new ones, ensuring a continuous loop of learning and optimization.
This process allows growth teams to be agile, data-driven and focused on maximizing impact with every experiment.
Types of Customer Feedback Used by Growth Teams
Growth teams use a variety of feedback sources, applying different types at each step of their process.
During Focus Area Selection
Before the quarter begins, the growth team collects feedback from multiple sources like surveys, support tickets, live chat, marketing channels, feature request boards, and analytics tools to identify gaps and opportunities.
They ask questions with analytics to identify steps in the user journey that cause issues and look at feature requests to spot popular or missed existing features.
While Brainstorming Initial Experiments
After choosing a focus area, the team gathers detailed customer feedback related to it, such as NPS mentions, support tickets, and Google Analytics data related to the area, looking for reasons for underperformance.
They prioritize experiments based on potential impact, ease of implementation, and likelihood of success.
Iterating on Experiments
The team enters a cycle of measuring results, learning, and re-prioritizing to launch new experiments quickly, often leaning on results and customer interviews for decision-making.
Ease of process organization is key, so well-organized teams can launch more experiments within a quarter.
Organizing and Scaling Experiments
Well-organized feedback processes allow growth teams to rapidly launch and iterate on more experiments within a quarter. By staying agile and responsive to customer insights, they can quickly implement changes that enhance the product and drive growth.
Key Stages of Feedback Utilization
Identifying Improvements: At the start of each quarter, the team collects feedback from various sources, such as surveys, support tickets, and analytics, to identify potential areas for optimization. This feedback helps them target specific areas for improvement, like enhancing user onboarding or reducing churn.
Prioritizing Experiments: Once improvement areas are identified, the team conducts user interviews and reviews feature request boards to prioritize experiments that are most likely to have a significant impact. They focus on experiments that are easy to implement and have a high likelihood of success.
Iterating on Feedback: As experiments are conducted, the team continuously measures results and gathers ongoing feedback to refine their strategies. This iterative process allows them to optimize their approach and quickly launch new experiments based on real-time insights.
Closing the Loop: After implementing changes, the team uses post-implementation surveys and usage data to evaluate the effectiveness of their efforts. This feedback loop ensures that the product improvements align with user expectations and enhance overall satisfaction.
The Importance of Customer Feedback for Growth Teams
Customer feedback is incredibly important for growth teams because it helps them find the right balance between keeping customers happy and driving business growth. Listening to what users have to say can reveal issues, highlight areas for improvement and guide decisions that make the product better for everyone.
While it’s true that the sheer amount of feedback can be overwhelming, having the right processes and tools in place can make a world of difference. When feedback is organized and managed well, it becomes much easier to spot trends, prioritize what needs attention, and take action. This means that the most valuable insights don’t get lost in the shuffle.
For growth teams, feedback isn’t just something to react to—it’s a goldmine of opportunities to make meaningful improvements. By regularly integrating what customers are saying into their strategies, growth teams can ensure that their work is always in tune with what users really want and need.
Conclusion
In conclusion, customer feedback serves as the backbone of any successful growth strategy. For growth teams, it’s more than just gathering opinions, it's about transforming those knowledge into actionable strategies that drive real results. By staying closely attuned to customer needs and continuously refining their approach through structured experimentation, growth teams can build products that not only meet but exceed user expectations.
This relentless focus on feedback not only ensures that business goals are met but also fosters deeper connections with customers, paving the way for long-term success and sustained growth.